Contents
What are the most effective ways to educate parents and caregivers about tick-borne diseases in children?
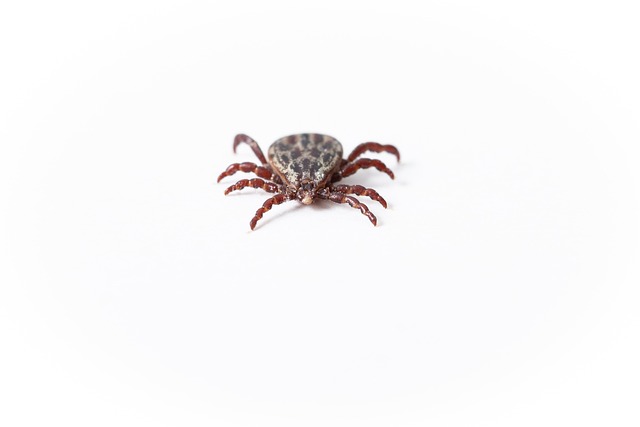
What are Tick-Borne Diseases?
Tick-borne diseases, also known as tick-associated diseases, are infections transmitted to humans and animals by a tick bite. Ticks are small arachnids, related to spiders and scorpions, that feed on the blood of their host. Ticks are known to spread diseases such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis and babesiosis. In children, tick-borne diseases can cause a range of symptoms depending on the type of illness.
Tick-Borne Diseases in Children: Symptoms
Common symptoms of tick-borne diseases in children include fever, fatigue, achy muscles, chills, headache, joint pain and rash. Additional symptoms may include confusion, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck and swollen lymph nodes. It is important to pay close attention to these signs, as some tick-borne diseases can have serious and long-term effects, especially if left untreated.
Prevention & Treatment of Tick-Borne Diseases
The best way for children to prevent tick-borne diseases is to avoid contact with ticks. This can be achieved by avoiding areas where ticks are found, such as wooded areas, long grass and areas with animals. When spending time outside, wearing long clothing and protective gear can reduce the chances of coming into contact with ticks.
Tick-borne diseases can be treated with antibiotics or antivirals, depending on the type of infection. But it is important to seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of the symptoms associated with tick-borne diseases in order to receive the most effective treatment.
Tick-Borne Diseases in Children: Health Risks
Children who become infected with tick-borne diseases can experience a number of health risks, including long-term illness and even death. Infections can cause severe joint pain, paralysis and even brain damage, in some cases. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of tick-borne diseases, seek immediate medical attention and follow all prevention tips to reduce the risk of infection.